KUALA LUMPUR, April 16 — Donating blood is a selfless act that many may not realise is crucial for a country’s healthcare system.
Your blood is essential to help patients survive surgeries, operations, cancer treatments, chronic illnesses and traumatic injuries.
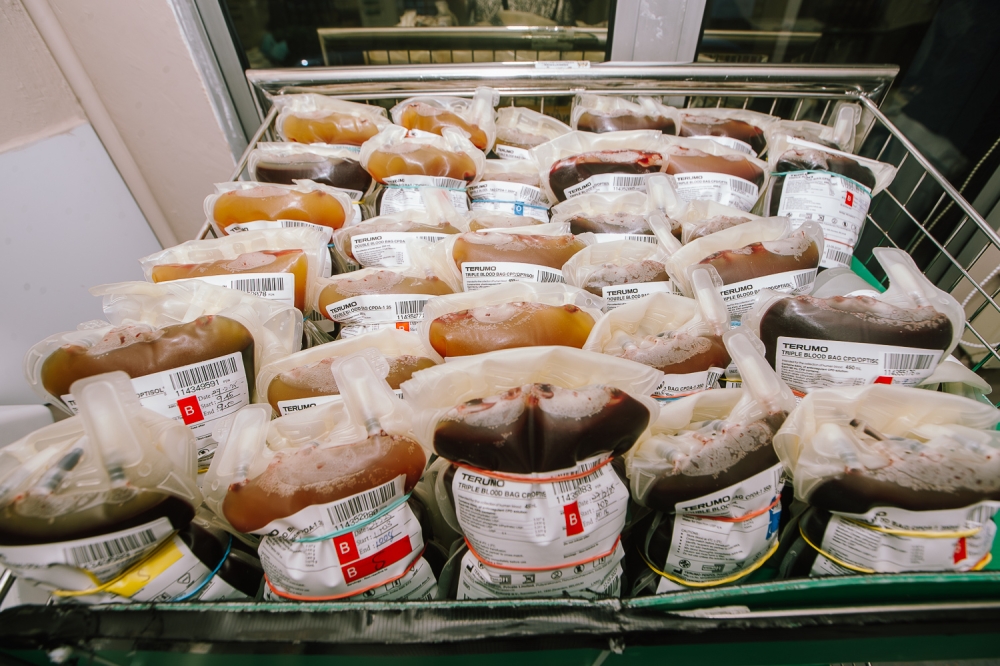

Blood storage and the importance of donation
The storage duration of blood components varies:
- Whole blood: Up to 35 days
- Plasma: Up to 1
- Red blood cells: Up to 42 days
- Platelets: Only 5 days
Blood donation provides essential components such as red and white blood cells, platelets and plasma, all of which play a vital role in medical treatments.
Cancer patients, for instance, often require transfusions to replenish platelets after undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Since these treatments can compromise bone marrow function, leading to reduced blood cell production, transfusions help prevent complications that could affect vital organs like the kidneys, spleen and liver.
There are two primary types of blood donation: whole blood donation and apheresis donation.
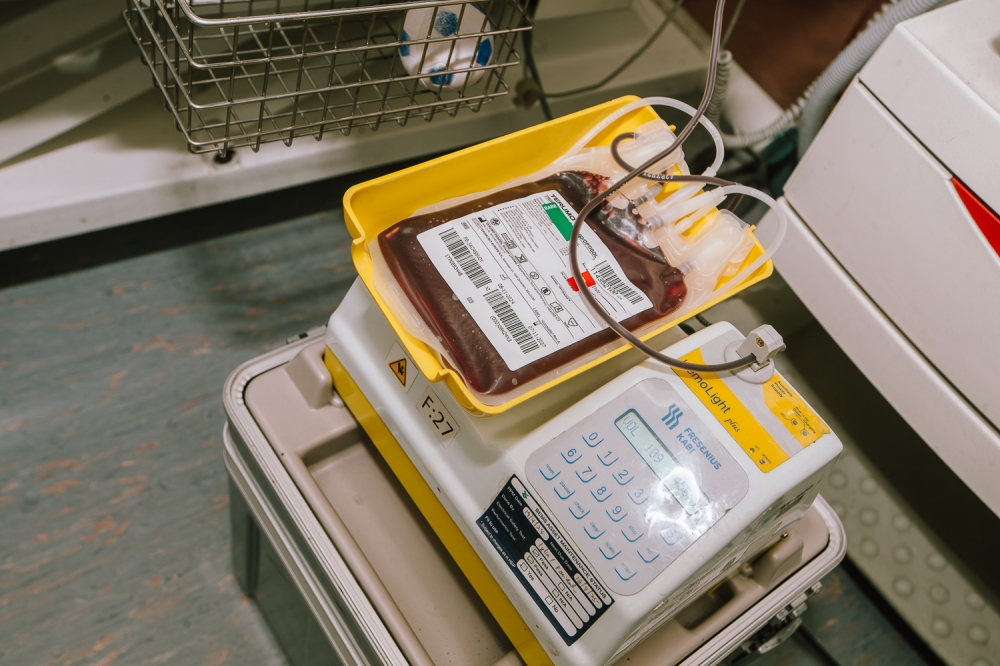

Whole blood donation
Whole blood refers to blood in its complete form not separated into various components.
This is the most common type of blood donation.
It takes around 10 minutes or less to fill up a 350 or 450ml bag.
This is approximately 8 to 12 per cent of the blood volume in the body.
It is commonly used for patients with massive blood loss or during surgeries for accident victims.
You can donate every three months or 12 weeks.
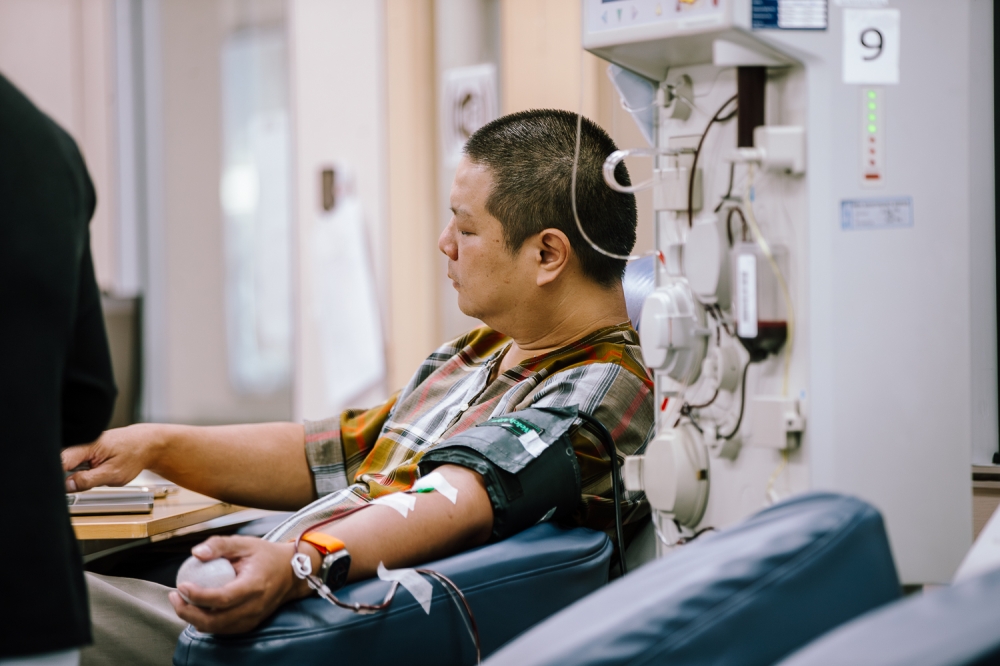
Apheresis donation
Human blood is made up of four components: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma.
Apheresis uses a centrifuge that separates blood into its components by density.
In Malaysia, the apheresis procedure uses one needle to transfer the blood in and out of the body. Some others use two.
A centrifuge machine draws blood from your body and spins the blood to separate its elements. The machine sets aside certain elements either plasma, platelets and red or white blood cells.
Once that is done, the remaining blood elements are returned to your body.
Benefits of apheresis are that it allows a much larger number of platelets to be collected from a single donor and minimises patients’ exposure to multiple donors’ blood.
Whole blood can be stored for up to 35 days.
Although plasma can be stored for up to three years, red blood cells can only be stored for up to 42 days and platelets only for up to 5 days.
Therefore, it is vital to maintain a high and stable level of blood donations.
When blood donation activity is low or volatile, healthcare services that depend upon blood transfusions may be negatively affected.
Blood types
There are four major blood groups determined by the presence or absence of two antigens, A and B, on the surface of red blood cells.
In addition to the A and B antigens, there is a protein called the Rh factor, which can be either present (+) or absent (–), creating the 8 most common blood types (A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, AB-).
Type O negative are universal donors meaning anyone can receive their blood without complications.
According to the Red Cross, type O is usually in short supply and in high demand by hospitals because it is the most common blood type and is the universal blood type needed for emergency transfusions and for immune deficient infants.
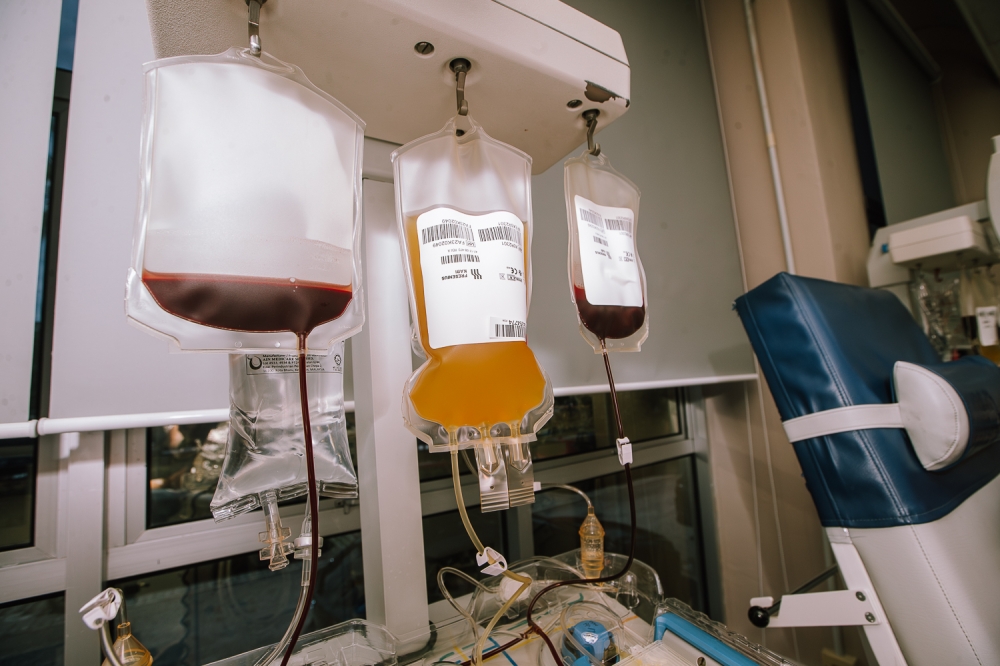

Platelets and plasma
Platelets help your body create clots to stop bleeding.
Platelet donations are critical for patients who are fighting cancer, chronic diseases and traumatic injuries.
The collection process is unique and a bit different than whole blood donations.
Both arms are involved.
One arm is used to send blood through the apheresis process using a sterile centrifuge.
The centrifuge separates the red blood cells from the platelets.
The heavier red cells sink to the bottom during the process.
These red blood cells are returned to you through the other arm.
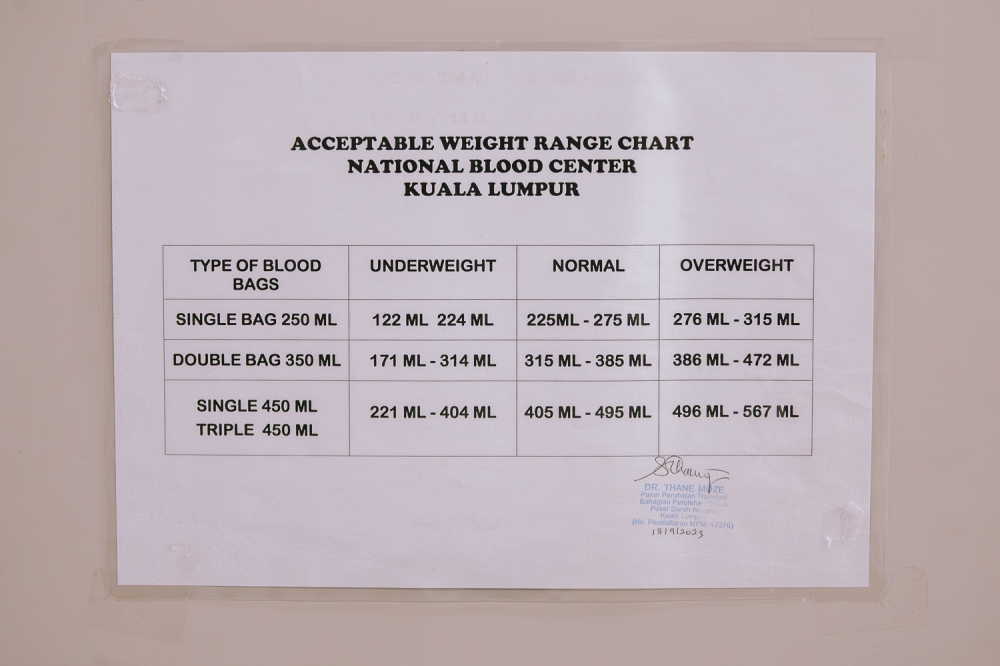
During a plasma donation, called plasmapheresis, blood is drawn from one arm and sent to the centrifuge that separates out the plasma.
The red blood cells and platelets are then returned to you in the same arm.
Plasma is used to help patients with severe burns, cancer or other potentially life-threatening conditions.
Blood donation is a continuous necessity with limited storage lifespans and ongoing demands from hospitals making regular donations a necessity.

















